Why data tagging?
Data tagging provides an identity to your data by associating it with metadata making it much easier to find and secure.
The New Oil
With the volume of data organizations store, a strategy is needed to tag and organize data efficiently.
Below are a few data tagging models that most organizations follow:
- Hierarchical Model
- Organize tags into a hierarchical model, with broader categories at the top and specific tags at the bottom
- Flat Model
- Each tag is equally important and no inherent relationship between tags
- Segment model
- Involves tagging data based on segments
- Jargon model
- Jargon recognizable within an organization or department that can be used for tagging
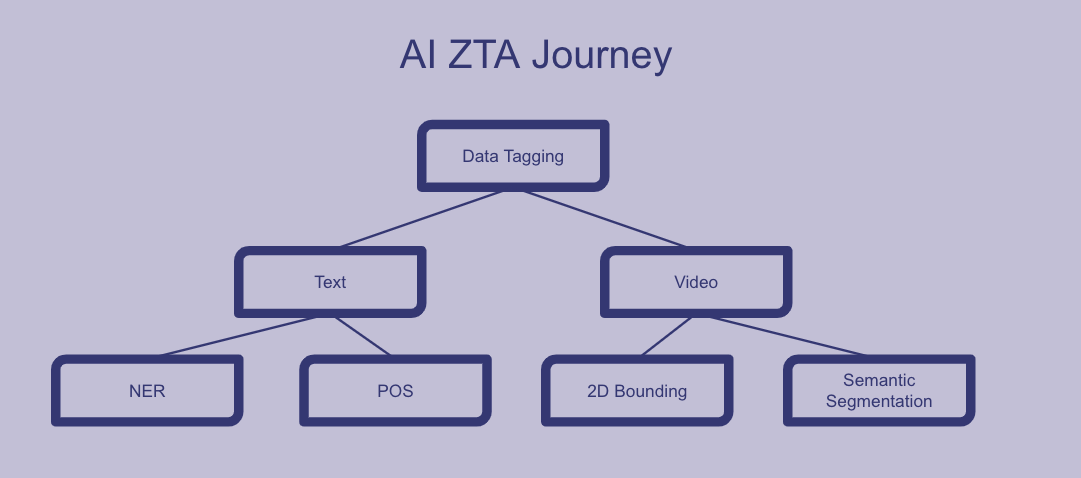
Data tagging can be classified into different types based on the format of the data being tagged. Below is an example of different types and each of the types can be further classified based on functionality.
- NER – identifies entitles (names, places and objects in a body of text)
- POS – associating words in a sentence
- 2D bounding – drawing a boundary around an object in order to make it recognizable
- Semantic Segmentation – tagging every individual pixel in an image
Recommended Data Tagging/Classification Journey steps:
- Identify data types/usage needs
- Data type: integers (whole numbers); floating-point numbers (3.14); strings (text…ex: “Hello World’); Boolean (true/false); character (single letters); or array (collection of data)
- Gather input from relevant stakeholders
- A well-defined nomenclature helps employees navigate and retrieve files
- Must be recognizable to the end user
- Use keywords, departments, projects, managers, team or other relevant identifiers
- Construct a model
- Data tagging model gives structure to data and contributes towards data classification
- Please refer to the next page for the 4 different data tagging models
- Conduct usability evaluations
- Take into account ease of accessibility and time spent retrieving files
- Automate data tagging process
Tagging vs. Classification
- Tagging is the labeling of data based on meta details (intends to improve accessibility and organization)
- Classification is done based on the level of sensitivity of file contents, intends to secure sensitive data and can be used to flag sensitive data by data loss prevention tools
Red Hat Solutions
OCP Secrets
- Red Hat’s data classification feature
- Use secrets to securely store sensitive data in conjunction with OCP RBAC (this is crucial for managing data governance and compliance within a containerized environment
OCP “Red Hat Discovery” and “Node Feature Discovery Operator”
- Data discovery tools
- Collects and scans information about OCP cluster including details about deployed applications, nodes, and system configurations
- The discovery operator automatically detects hardware features on cluster nodes, adding relevant labels for easier management
OCP “Label Studio”
- Labels diverse data types like images, text, audio and video, enabling users to create bounding boxes, polygons and other annotations
- Simplifies the data labeling process, enabling users to annotate datasets quickly and accurately
